PhysicsGenerator
- class deepinv.physics.generator.PhysicsGenerator(step=<function PhysicsGenerator.<lambda>>, rng: ~torch._C.Generator | None = None, device='cpu', dtype=torch.float32, **kwargs)[source]
Bases:
ModuleBase class for parameter generation of physics parameters.
Physics generators are used to generate the parameters \(\theta\) of (parameter-dependent) forward operators.
Generators can be summed to create larger generators via
deepinv.physics.generator.PhysicsGenerator.__add__(), or mixed to create a generator that randomly selects them viadeepinv.physics.generator.GeneratorMixture().- Parameters:
step (Callable) – a function that generates the parameters of the physics, e.g., the filter of the
deepinv.physics.Blur(). This function should return the parameters in a dictionary with the corresponding key and value pairs.rng (torch.Generator (Optional)) – a pseudorandom random number generator for the parameter generation. If
None, the default Generator of PyTorch will be used.device (str) – cpu or cuda
dtype (torch.dtype) – the data type of the generated parameters
- Examples:
Generating blur and noise levels:
>>> import torch >>> from deepinv.physics.generator import MotionBlurGenerator, SigmaGenerator >>> # combine a PhysicsGenerator for blur and noise level parameters >>> generator = MotionBlurGenerator(psf_size = (3, 3), num_channels = 1) + SigmaGenerator() >>> params_dict = generator.step(batch_size=1, seed=0) # dict_keys(['filter', 'sigma']) >>> print(params_dict['filter']) tensor([[[[0.0000, 0.1006, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.8994, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]]]) >>> print(params_dict['sigma']) tensor([0.2532])
- __add__(other)[source]
Creates a new generator from the sum of two generators.
- Parameters:
other (Generator) – the other generator to be added.
- Returns:
A new generator that generates a larger dictionary with parameters of the two generators.
- rng_manual_seed(seed: int | None = None)[source]
Sets the seed for the random number generator.
- Parameters:
seed (int) – the seed to set for the random number generator. If not provided, the current state of the random number generator is used. Note: The torch.manual_seed is triggered when a the random number generator is not initialized.
Examples using PhysicsGenerator:
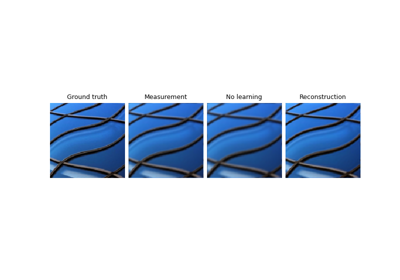
Imaging inverse problems with adversarial networks
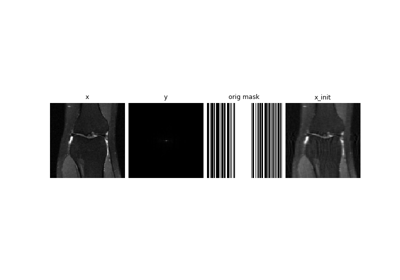
Self-supervised MRI reconstruction with Artifact2Artifact