Note
New to DeepInverse? Get started with the basics with the 5 minute quickstart tutorial..
Self-supervised denoising with the SURE loss.#
This example shows you how to train a denoiser network in a fully self-supervised way, i.e., using noisy images only via the SURE loss, which exploits knowledge about the noise distribution.
The SURE loss for Poisson denoising acts as an unbiased estimator of the supervised loss and is computed as:
where \(R\) is the trainable network, \(y\) is the noisy image with \(m\) pixels, \(b\) is a Bernoulli random variable taking values of -1 and 1 each with a probability of 0.5, \(\tau\) is a small positive number, and \(\odot\) is an elementwise multiplication.
from pathlib import Path
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import deepinv as dinv
from deepinv.utils import get_data_home
from deepinv.models.utils import get_weights_url
Setup paths for data loading and results.#
BASE_DIR = Path(".")
DATA_DIR = BASE_DIR / "measurements"
CKPT_DIR = BASE_DIR / "ckpts"
ORIGINAL_DATA_DIR = get_data_home()
# Set the global random seed from pytorch to ensure reproducibility of the example.
torch.manual_seed(0)
device = dinv.utils.get_device()
Selected GPU 0 with 4064.25 MiB free memory
Load base image datasets#
In this example, we use the MNIST dataset as the base image dataset.
operation = "denoising"
train_dataset_name = "MNIST"
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(
root=ORIGINAL_DATA_DIR, train=True, transform=transform, download=True
)
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(
root=ORIGINAL_DATA_DIR, train=False, transform=transform, download=True
)
Generate a dataset of noisy images#
We generate a dataset of noisy images corrupted by Poisson noise.
Note
We use a subset of the whole training set to reduce the computational load of the example.
We recommend to use the whole set by setting n_images_max=None to get the best results.
# defined physics
physics = dinv.physics.Denoising(dinv.physics.PoissonNoise(0.1))
# Use parallel dataloader if using a GPU to speed up training,
# otherwise, as all computes are on CPU, use synchronous data loading.
num_workers = 4 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 0
n_images_max = (
100 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 5
) # number of images used for training
measurement_dir = DATA_DIR / train_dataset_name / operation
deepinv_datasets_path = dinv.datasets.generate_dataset(
train_dataset=train_dataset,
test_dataset=test_dataset,
physics=physics,
device=device,
save_dir=measurement_dir,
train_datapoints=n_images_max,
test_datapoints=n_images_max,
num_workers=num_workers,
dataset_filename="demo_sure",
)
train_dataset = dinv.datasets.HDF5Dataset(path=deepinv_datasets_path, train=True)
test_dataset = dinv.datasets.HDF5Dataset(path=deepinv_datasets_path, train=False)
Dataset has been saved at measurements/MNIST/denoising/demo_sure0.h5
Set up the denoiser network#
We use a simple U-Net architecture with 2 scales as the denoiser network.
model = dinv.models.ArtifactRemoval(
dinv.models.UNet(in_channels=1, out_channels=1, scales=2).to(device)
)
Set up the training parameters#
We set deepinv.loss.SurePoissonLoss as the training loss.
Note
There are SURE losses for various noise distributions. See also deepinv.loss.SureGaussianLoss
for Gaussian noise and deepinv.loss.SurePGLoss for mixed Poisson-Gaussian noise.
Note
We use a pretrained model to reduce training time. You can get the same results by training from scratch for 10 epochs.
epochs = 1 # choose training epochs
learning_rate = 5e-4
batch_size = 32 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 1
# choose self-supervised training loss
loss = dinv.loss.SurePoissonLoss(gain=0.1)
# choose optimizer and scheduler
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=1e-8)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=int(epochs * 0.8) + 1)
# start with a pretrained model to reduce training time
file_name = "ckp_10_demo_sure.pth"
url = get_weights_url(model_name="demo", file_name=file_name)
ckpt = torch.hub.load_state_dict_from_url(
url, map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage, file_name=file_name
)
# load a checkpoint to reduce training time
model.load_state_dict(ckpt["state_dict"])
optimizer.load_state_dict(ckpt["optimizer"])
Train the network#
To simulate a realistic self-supervised learning scenario, we do not use any supervised metrics for training, such as PSNR or SSIM, which require clean ground truth images.
Tip
We can use the same self-supervised loss for evaluation, as it does not require clean images,
to monitor the training process (e.g. for early stopping). This is done automatically when metrics=None and early_stop>0 in the trainer.
verbose = True # print training information
train_dataloader = DataLoader(
train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=True
)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(
test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=False
)
# Initialize the trainer
trainer = dinv.Trainer(
model=model,
physics=physics,
epochs=epochs,
scheduler=scheduler,
losses=loss,
optimizer=optimizer,
device=device,
train_dataloader=train_dataloader,
eval_dataloader=test_dataloader,
compute_eval_losses=True, # use self-supervised loss for evaluation
early_stop_on_losses=True, # stop using self-supervised eval loss
metrics=None, # no supervised metrics
early_stop=2, # early stop using the self-supervised loss on the test set
plot_images=True,
save_path=str(CKPT_DIR / operation),
verbose=verbose,
show_progress_bar=False, # disable progress bar for better vis in sphinx gallery.
)
# Train the network
model = trainer.train()
/local/jtachell/deepinv/deepinv/deepinv/training/trainer.py:1354: UserWarning: non_blocking_transfers=True but DataLoader.pin_memory=False; set pin_memory=True to overlap host-device copies with compute.
self.setup_train()
The model has 444737 trainable parameters
Train epoch 0: TotalLoss=0.002
Eval epoch 0: TotalLoss=0.002
Best model saved at epoch 1
Test the network#
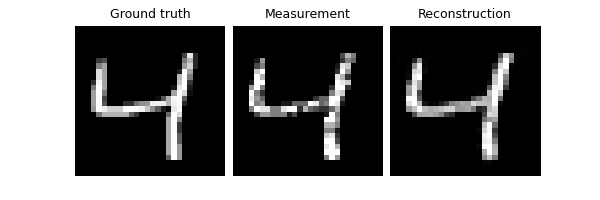
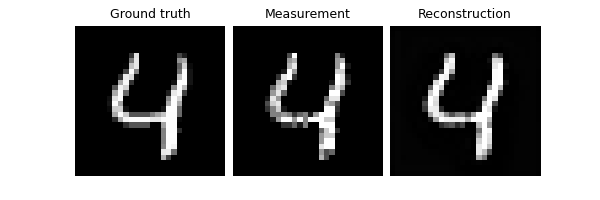
We now assume that we have access to a small test set of clean images to evaluate the performance of the trained network. and we compute the PSNR between the denoised images and the clean ground truth images.
trainer.test(test_dataloader, metrics=dinv.metric.PSNR())

/local/jtachell/deepinv/deepinv/deepinv/training/trainer.py:1546: UserWarning: non_blocking_transfers=True but DataLoader.pin_memory=False; set pin_memory=True to overlap host-device copies with compute.
self.setup_train(train=False)
Eval epoch 0: TotalLoss=0.002, PSNR=26.088, PSNR no learning=19.487
Test results:
PSNR no learning: 19.487 +- 1.628
PSNR: 26.088 +- 1.411
{'PSNR no learning': 19.487266845703125, 'PSNR no learning_std': 1.6277921401540443, 'PSNR': 26.088257446289063, 'PSNR_std': 1.4109794353301222}
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.650 seconds)