Note
New to DeepInverse? Get started with the basics with the 5 minute quickstart tutorial..
Loading scientific images#
This example presents the various input/output functions provided by DeepInverse for handling medical and scientific imaging formats. We demonstrate loading and plotting from DICOM, NIfTI, ISMRMRD, PyTorch, NumPy and raster data sources.
import deepinv as dinv
1. Load DICOM#
DICOM files are commonly used in clinical imaging. We can fetch and load them
directly using deepinv.utils.load_dicom(). Here, we demonstrate on a
demo DICOM from the Internet.
This function requires pydicom. Install it with pip install pydicom.
Note
You can also call the io functions directly as dinv.io.load_...
x = dinv.utils.io.load_dicom(
dinv.utils.io.load_url(
"https://github.com/robyoung/dicom-test-files/raw/refs/heads/master/data/pydicom/693_J2KI.dcm"
)
) # (1,H,W)
dinv.utils.plot({"dicom": x.unsqueeze(0)})

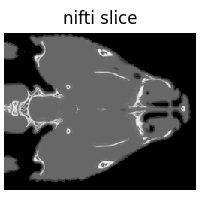
2. Load NIfTI#
NIfTI files are often used for volumetric neuroimaging data. We load them using deepinv.utils.load_nifti().
Since nibabel doesn’t support file buffers, we download a sample volume first.
This function requires nibabel. Install it with pip install nibabel.
import requests
save_path = dinv.utils.get_data_home() / "tmp.nii.gz"
with open(save_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(
requests.get(
"https://github.com/neurolabusc/niivue-images/raw/refs/heads/main/Iguana.nii.gz"
).content
)
x = dinv.utils.io.load_nifti(save_path).unsqueeze(0) # (1, H, W, D)
x = x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2] # take central slice, (1,H,W)
dinv.utils.plot({"nifti slice": x.unsqueeze(0)})
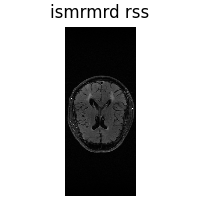
3. Load ISMRMRD#
ISMRMRD is a standard raw MRI k-space format. We load a k-space slice using deepinv.utils.load_ismrmd()
and compute a root-sum-of-squares reconstruction.
y = dinv.utils.io.load_ismrmd(
dinv.utils.io.load_url(
dinv.utils.demo.get_image_url("demo_fastmri_brain_multicoil.h5")
),
data_name="kspace",
data_slice=0,
) # (2,N,H,W) where N is coils
rss = dinv.physics.MultiCoilMRI(img_size=y.shape[-2:]).A_adjoint(
y.unsqueeze(0), rss=True
) # (1,2,H,W)
dinv.utils.plot({"ismrmrd rss": rss})
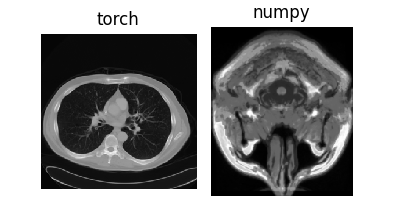
4. Load tensors and arrays#
We provide helper functions for loading tensors and arrays directly, for example provided
in the DeepInverse HuggingFace demo repository <https://huggingface.co/datasets/deepinv/images>.
x = dinv.utils.io.load_torch(
dinv.utils.load_url(dinv.utils.demo.get_image_url("CT100_256x256_0.pt"))
) # (1,1,H,W)
y = dinv.utils.io.load_np(
dinv.utils.load_url(
dinv.utils.demo.get_image_url("brainweb_t1_ICBM_1mm_subject_0_slice_0.npy")
)
) # (H,W)
dinv.utils.plot({"torch": x, "numpy": y.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)})
6. Load raster images#
Raster formats (e.g. GeoTIFF, COSAR) can be streamed with patches.
See deepinv.utils.load_raster() for patch options.
This function requires rasterio. Install it with pip install rasterio.
patches = dinv.utils.io.load_raster(
dinv.utils.io.load_url(
"https://download.osgeo.org/geotiff/samples/spot/chicago/SP27GTIF.TIF"
),
patch=500,
patch_start=(200, 200),
)
x = next(patches) # Stream patch
dinv.utils.plot({"raster": x.unsqueeze(0)})

Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 12.678 seconds)

