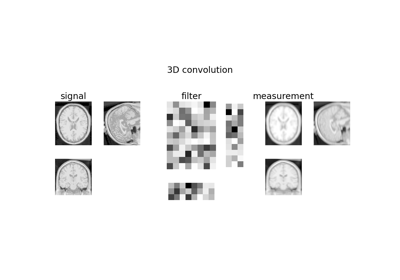
DiffractionBlurGenerator3D#
- class deepinv.physics.generator.DiffractionBlurGenerator3D(psf_size, num_channels=1, zernike_index=tuple(range(4, 12)), fc=0.2, kb=0.25, max_zernike_amplitude=0.15, pupil_size=(512, 512), apodize=False, random_rotate=False, stepz_pixel=1.0, index_convention='noll', rng=None, device='cpu', dtype=torch.float32, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
PSFGenerator3D diffraction limited kernels using Zernike decomposition of the phase mask (Fresnel/Fraunhoffer diffraction theory).
This method simulates the propagation of the wavefront from the pupil plane (frequency domain) to multiple defocus planes in the image space. The pupil function is constructed using a Zernike polynomial decomposition of the wavefront aberrations, see
deepinv.physics.generator.DiffractionBlurGeneratorfor more details.At each depth \(z\), the pupil function is modulated by a phase term corresponding to the axial wave vector \(k_z\), which is derived from the dispersion relation of light in free space.
\[k_z = \sqrt{k_{\text{total}}^2 - k_{\text{lateral}}^2}\]where \(k_{\text{total}}\) is the total wave number (
kb) and \(k_{\text{lateral}}\) is the lateral wave vector component. The pupil function at depth \(z\) is given by:\[P(x, y, z) = P(x, y, 0) \cdot \exp \left( - i 2 \pi \cdot k_z \cdot z \right)\]And the depth planes are sampled according to the
stepz_pixelparameter, which defines the ratio between the physical size of the \(z\) direction to that in the \(x/y\) direction of the voxels in the 3D image.The 3D PSF is then computed by square modulus of Fourier transform of the modulated pupil function at each depth plane, followed by normalization across the spatial dimensions.
Note
This class uses
deepinv.physics.generator.DiffractionBlurGeneratorunder the hood to generate the pupil function at \(z=0\). Refer to its documentation for more details.- Parameters:
psf_size (tuple) – give in the order
(depth, height, width)the size of the PSF to generate.num_channels (int) – number of channels. Default to
1.zernike_index (tuple[int, ...], tuple[tuple[int, int], ...]) –
activated Zernike coefficients in the following
index_conventionconvention. It can be either:a tuple of
intcorresponding to the Noll or ANSI indices, in which case theindex_conventionparameter is required to interpret them correctly.a tuple of
tuple[int, int]corresponding to the standard radial-angular indexing \((n,m)\). In this case, theindex_conventionparameter is ignored.
Defaults to
(4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11), correspond to radial ordernfrom 2 to 3 (included) and the spherical aberration. These correspond to the following aberrations: defocus, astigmatism, coma, trefoil and spherical aberration.fc (float) – cutoff frequency
(NA/emission_wavelength) * pixel_size. Should be in[0, 1/4]to respect Shannon, defaults to0.2.kb (float) – wave number
(NI/emission_wavelength) * pixel_sizeor(NA/NI) * fc. Must be greater thanfc. Defaults to0.3.max_zernike_amplitude (float) – maximum amplitude of Zernike coefficients. Defaults to 0.15.
pupil_size (tuple[int]) – pixel size to synthesize the super-resolved pupil. The higher the more precise, defaults to
(512, 512). If anintis given, a square pupil is considered.apodize (bool) – whether to apodize the PSF to reduce ringing effects. Defaults to
False.random_rotate (bool) – whether to randomly rotate the PSF in the xy plane. Defaults to
False.stepz_pixel (float) – Ratio between the physical size of the \(z\) direction to that in the \(x/y\) direction of the voxels in the 3D image. Defaults to
1.0.index_convention (str) – convention for the Zernike indices, either
'noll'(default) or'ansi'.rng (torch.Generator) – random number generator (default to
None).device (str) – device (default to
'cpu').dtype (type) – data type (default to
torch.float32).kwargs – additional arguments for
deepinv.physics.generator.DiffractionBlurGenerator.
Note
NA: numerical aperture,NI: refraction index of the immersion medium,emission_wavelength: wavelength of the light,pixel_size: physical size of the pixels in the \(xy\) plane in the same unit asemission_wavelength.
- Examples:
>>> import torch >>> from deepinv.physics.generator import DiffractionBlurGenerator3D >>> generator = DiffractionBlurGenerator3D((21, 51, 51), stepz_pixel = 2, zernike_index=(3,), index_convention='ansi') >>> print(generator.zernike_polynomials) # list of Zernike polynomials used ['Zernike(n = 2, m = -2) -- Oblique Astigmatism'] >>> dict = generator.step() >>> filter = dict['filter'] >>> print(filter.shape) torch.Size([1, 1, 21, 51, 51]) >>> batch_size = 2 >>> n_zernike = len(generator.generator2d.zernike_index) >>> dict = generator.step(batch_size=batch_size, coeff=0.1 * torch.rand(batch_size, n_zernike)) >>> dict.keys() dict_keys(['filter', 'pupil', 'coeff'])
- step(batch_size=1, coeff=None, angle=None, seed=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Generate a batch of PSF with a batch of Zernike coefficients
- Parameters:
batch_size (int) – number of PSFs to generate.
coeff (torch.Tensor) – tensor of size (batch_size x len(zernike_index)) containing the Zernike coefficients. If
None, random coefficients are generated.seed (int) – the seed for the random number generator.
- Returns:
dictionary with keys
filter: tensor of size(batch_size x num_channels x psf_size[0] x psf_size[1])batch of PSFs,pupil: the pupil function,coeff: list of sampled Zernike coefficients in this realization,angle: the random rotation angles in degrees ifrandom_rotateisTrue, nothing otherwise.
- Return type: