SupLoss#
- class deepinv.loss.SupLoss(metric=None)[source]#
Bases:
LossStandard supervised loss
The supervised loss is defined as
\[\frac{1}{n}\|x-\inverse{y}\|^2\]where \(\inverse{y}\) is the reconstructed signal and \(x\) is the ground truth target of \(n\) elements.
By default, the error is computed using the MSE metric, however any other metric (e.g., \(\ell_1\)) can be used as well. If called with arguments
x_net, x, this is simply a wrapper for the metricmetric.- Parameters:
metric (Metric, torch.nn.Module) – metric used for computing data consistency, which is set as the mean squared error by default.
- forward(x_net, x, **kwargs)[source]#
Computes the loss.
- Parameters:
x_net (torch.Tensor) – Reconstructed image :math:inverse{y}.
x (torch.Tensor) – Target (ground-truth) image.
- Returns:
(
torch.Tensor) loss.- Return type:
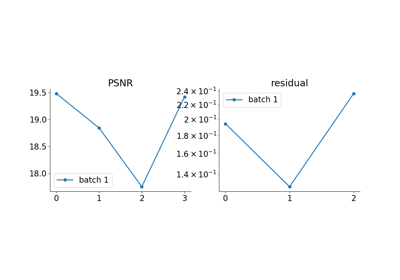
Examples using SupLoss:#
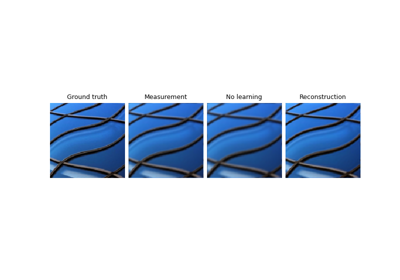
Imaging inverse problems with adversarial networks

Deep Equilibrium (DEQ) algorithms for image deblurring
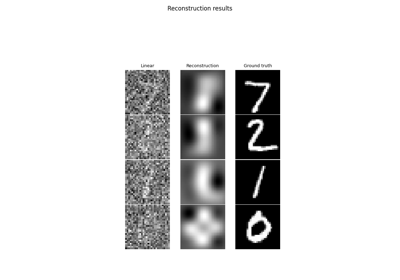
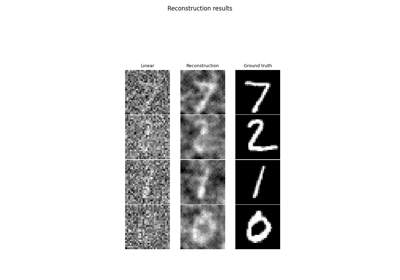
Learned Iterative Soft-Thresholding Algorithm (LISTA) for compressed sensing
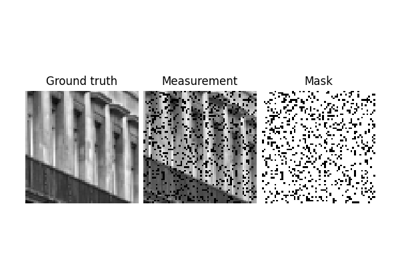
Unfolded Chambolle-Pock for constrained image inpainting