MRI#
- class deepinv.physics.MRI(mask=None, img_size=(320, 320), three_d=False, device='cpu', **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
MRIMixin,DecomposablePhysicsSingle-coil accelerated 2D or 3D magnetic resonance imaging.
The linear operator operates in 2D slices or 3D volumes and is defined as
\[y = MFx\]where \(M\) applies a mask (subsampling operator), and \(F\) is the 2D or 3D discrete Fourier Transform. This operator has a simple singular value decomposition, so it inherits the structure of
deepinv.physics.DecomposablePhysicsand thus have a fast pseudo-inverse and prox operators.The complex images \(x\) and measurements \(y\) should be of size (B, C,…, H, W) with C=2, where the first channel corresponds to the real part and the second channel corresponds to the imaginary part. The
...is an optional depth dimension for 3D MRI data.A fixed mask can be set at initialisation, or a new mask can be set either at forward (using
physics(x, mask=mask)) or usingupdate.Note
We provide various random mask generators (e.g. Cartesian undersampling) that can be used directly with this physics. See e.g.
deepinv.physics.generator.mri.RandomMaskGeneratorIf mask is not passed, a mask full of ones is used (i.e. no acceleration).Note
This physics is directly compatible with FastMRI data using
deepinv.datasets.FastMRISliceDataset. The dataset loads pairs of magnitude images and kspace(x, y)wherex = MRI().A_adjoint(y, mag=True, crop=True).- Parameters:
mask (torch.Tensor) – binary mask, where 1s represent sampling locations, and 0s otherwise. The mask size can either be (H,W), (C,H,W), (B,C,H,W), (B,C,…,H,W) where H, W are the image height and width, C is channels (which should be 2) and B is batch size.
img_size (tuple) – if mask not specified, flat mask of ones is created using
img_size, whereimg_sizecan be of any shape specified above. If mask provided,img_sizeis ignored.three_d (bool) – if
True, calculate Fourier transform in 3D for 3D data (i.e. data of shape (B,C,D,H,W) where D is depth).device (torch.device) – cpu or gpu.
- Examples:
Single-coil accelerated MRI operator with subsampling mask:
>>> from deepinv.physics import MRI >>> seed = torch.manual_seed(0) # Random seed for reproducibility >>> x = torch.randn(1, 2, 2, 2) # Define random 2x2 image >>> mask = 1 - torch.eye(2) # Define subsampling mask >>> physics = MRI(mask=mask) # Define mask at initialisation >>> physics(x) tensor([[[[ 0.0000, -1.4290], [ 0.4564, -0.0000]], [[ 0.0000, 1.8622], [ 0.0603, -0.0000]]]]) >>> physics = MRI(img_size=x.shape) # No subsampling >>> physics(x) tensor([[[[ 2.2908, -1.4290], [ 0.4564, -0.1814]], [[ 0.3744, 1.8622], [ 0.0603, -0.6209]]]]) >>> physics.update(mask=mask) # Update mask on the fly >>> physics(x) tensor([[[[ 0.0000, -1.4290], [ 0.4564, -0.0000]], [[ 0.0000, 1.8622], [ 0.0603, -0.0000]]]])
- A_adjoint(y, mask=None, mag=False, crop=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Adjoint operator.
Optionally perform crop and magnitude to match FastMRI data.
By default, crop and magnitude are not performed. By setting
mag=crop=True, the outputs will be consistent withdeepinv.datasets.FastMRISliceDataset.- Parameters:
y (torch.Tensor) – input kspace of shape (B,C,…,H,W)
mask (torch.Tensor) – optionally set mask on-the-fly.
mag (bool) – perform complex magnitude. This option is provided to match the original data of
deepinv.datasets.FastMRISliceDataset, such thatx = MRI().A_adjoint(y, mag=True).crop (bool) – if
True, crop last 2 dims of x to last 2 dims of img_size. This option is provided to match the original data ofdeepinv.datasets.FastMRISliceDataset, such thatx = MRI().A_adjoint(y, crop=True).
- noise(x, **kwargs)[source]#
Incorporates noise into the measurements \(\tilde{y} = N(y)\)
- Parameters:
x (torch.Tensor) – clean measurements
- Return torch.Tensor:
noisy measurements
- update_parameters(mask=None, check_mask=True, **kwargs)[source]#
Update MRI subsampling mask.
- Parameters:
mask (torch.nn.parameter.Parameter, torch.Tensor) – MRI mask
check_mask (bool) – check mask dimensions before updating
Examples using MRI:#
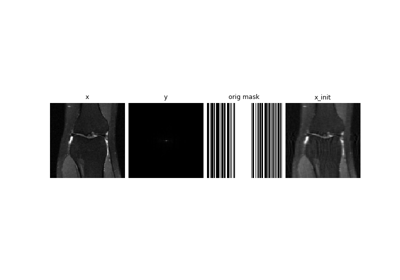
Self-supervised MRI reconstruction with Artifact2Artifact
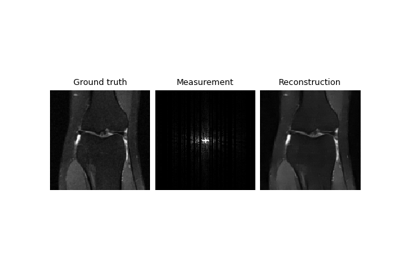
Self-supervised learning with Equivariant Imaging for MRI.