DRUNet#
- class deepinv.models.DRUNet(in_channels=3, out_channels=3, nc=(64, 128, 256, 512), nb=4, act_mode='R', downsample_mode='strideconv', upsample_mode='convtranspose', pretrained='download', pretrained_2d_isotropic=False, device=None, dim=2)[source]#
Bases:
DenoiserDRUNet denoiser network.
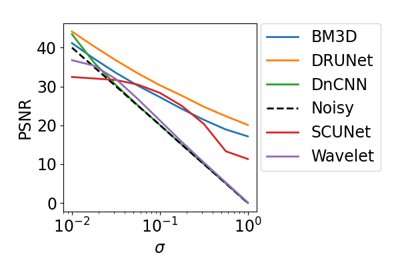
The network architecture is based on the paper Zhang et al.[1]. and has a U-Net like structure, with convolutional blocks in the encoder and decoder parts.
The network takes into account the noise level of the input image, which is encoded as an additional input channel.
A pretrained network for (in_channels=out_channels=1 or in_channels=out_channels=3) can be downloaded via setting
pretrained='download'.- Parameters:
in_channels (int) – number of channels of the input.
out_channels (int) – number of channels of the output.
nc (Sequence[int,int,int,int]) – number of channels per convolutional layer, the network has a fixed number of 4 scales with
nbblocks per scale (default:[64,128,256,512]).nb (int) – number of convolutional blocks per layer.
act_mode (str) – activation mode, “R” for ReLU, “L” for LeakyReLU “E” for ELU and “s” for Softplus.
downsample_mode (str) – Downsampling mode, “avgpool” for average pooling, “maxpool” for max pooling, and “strideconv” for convolution with stride 2.
upsample_mode (str) – Upsampling mode, “convtranspose” for convolution transpose, “pixelshuffle” for pixel shuffling, and “upconv” for nearest neighbour upsampling with additional convolution. “pixelshuffle” is not implemented for 3D.
pretrained (str, None) – use a pretrained network. If
pretrained=None, the weights will be initialized at random using Pytorch’s default initialization. Ifpretrained='download', the weights will be downloaded from an online repository (only available for the default architecture with 3 or 1 input/output channels). When building a 3D network, it is possible to initialize with 2D pretrained weights by usingpretrained='download_2d', which provides a good starting point for fine-tuning. Finally,pretrainedcan also be set as a path to the user’s own pretrained weights. See pretrained-weights for more details.pretrained_2d_isotropic (bool) – when loading 2D pretrained weights into a 3D network, whether to initialize the 3D kernels isotropically. By default the weights are loaded axially, i.e., by initializing the central slice of the 3D kernels with the 2D weights.
device (torch.device, str) – Device to put the model on.
dim (str, int) – Whether to build 2D or 3D network (if str, can be “2”, “2d”, “3D”, etc.)
- Examples:
>>> import deepinv as dinv >>> import torch >>> denoiser = dinv.models.DRUNet() >>> y = torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32) >>> sigma = 0.1 >>> with torch.no_grad(): ... denoised = denoiser(y, sigma)
- References:
- forward(x, sigma)[source]#
Run the denoiser on image with noise level \(\sigma\).
- Parameters:
x (torch.Tensor) – noisy image
sigma (float, torch.Tensor) – noise level. If
sigmais a float, it is used for all images in the batch. Ifsigmais a tensor, it must be of shape(batch_size,).
Examples using DRUNet:#

Random phase retrieval and reconstruction methods.

Building your diffusion posterior sampling method using SDEs