Prior#
- class deepinv.optim.Prior(g=None, *args, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
PotentialPrior term \(\reg{x}\).
This is the base class for the prior term \(\reg{x}\). As a child class from the Poential class, it comes with methods for computing \(\operatorname{prox}_{g}\) and \(\nabla \regname\). To implement a custom prior, for an explicit prior, overwrite \(\regname\) (do not forget to specify
self.explicit_prior = True)This base class is also used to implement implicit priors. For instance, in PnP methods, the method computing the proximity operator is overwritten by a method performing denoising. For an implicit prior, overwrite
gradorprox.Note
The methods for computing the proximity operator and the gradient of the prior rely on automatic differentiation. These methods should not be used when the prior is not differentiable, although they will not raise an error.
- Parameters:
g (Callable) – Prior function \(g(x)\).
Examples using Prior:#
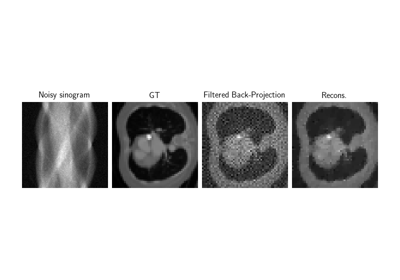
Low-dose CT with ASTRA backend and Total-Variation (TV) prior
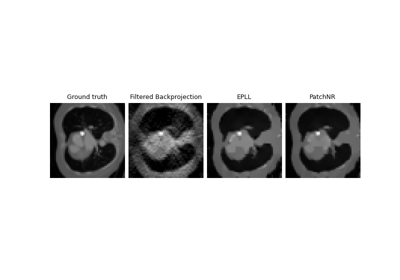
Patch priors for limited-angle computed tomography

Random phase retrieval and reconstruction methods.
Pattern Ordering in a Compressive Single Pixel Camera

PnP with custom optimization algorithm (Primal-Dual Condat-Vu)
Plug-and-Play algorithm with Mirror Descent for Poisson noise inverse problems.
Regularization by Denoising (RED) for Super-Resolution.

Deep Equilibrium (DEQ) algorithms for image deblurring
Learned Iterative Soft-Thresholding Algorithm (LISTA) for compressed sensing
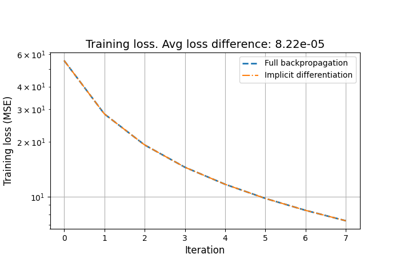
Reducing the memory and computational complexity of unfolded network training
Unfolded Chambolle-Pock for constrained image inpainting