Pansharpen#
- class deepinv.physics.Pansharpen(img_size, filter='bilinear', factor=4, srf='flat', noise_color=None, noise_gray=None, use_brovey=True, device='cpu', padding='circular', normalize=False, eps=1e-6, **kwargs)[source]#
Bases:
StackedLinearPhysicsPansharpening forward operator.
The measurements consist of a high resolution grayscale image and a low resolution RGB image, and are represented using
deepinv.utils.TensorList, where the first element is the RGB image and the second element is the grayscale image.By default, the downsampling is done with a gaussian filter with standard deviation equal to the downsampling, however, the user can provide a custom downsampling filter.
It is possible to assign a different noise model to the RGB and grayscale images.
- Parameters:
img_size (tuple[int]) – size of the high-resolution multispectral input image, must be of shape (C, H, W).
filter (torch.Tensor, str, None) – Downsampling filter. It can be ‘gaussian’, ‘bilinear’ or ‘bicubic’ or a custom
torch.Tensorfilter. IfNone, no filtering is applied.factor (int) – downsampling factor/ratio.
srf (str, tuple, list) – spectral response function of the decolorize operator to produce grayscale from multispectral. See
deepinv.physics.Decolorizefor parameter options. Defaults toflati.e. simply average the bands.use_brovey (bool) – if
True, use the Brovey method Vivone et al.[1]. to compute the pansharpening, otherwise use the conjugate gradient method.noise_color (torch.nn.Module) – noise model for the RGB image. It defaults to zero noise.
noise_gray (torch.nn.Module) – noise model for the grayscale image. It defaults to zero noise.
device (torch.device, str) – torch device.
padding (str) – options are
'valid','circular','replicate'and'reflect'. Ifpadding='valid'the blurred output is smaller than the image (no padding) otherwise the blurred output has the same size as the image.normalize (bool) – if
True, normalize the downsampling operator to have unit norm.eps (float) – small value to avoid division by zero in the Brovey method.
- Examples:
Pansharpen operator applied to a random 32x32 image:
>>> from deepinv.physics import Pansharpen >>> import torch >>> x = torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32) # Define random 32x32 color image >>> physics = Pansharpen(img_size=x.shape[1:], device=x.device) >>> x.shape torch.Size([1, 3, 32, 32]) >>> y = physics(x) >>> y[0].shape torch.Size([1, 3, 8, 8]) >>> y[1].shape torch.Size([1, 1, 32, 32])
- References:
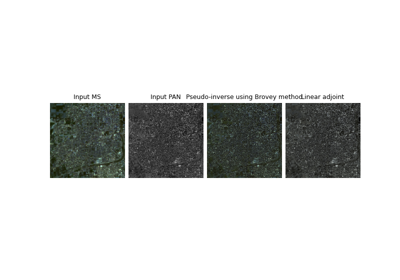
- A_dagger(y, **kwargs)[source]#
If the Brovey method is used, compute the classical Brovey solution, otherwise compute the conjugate gradient solution.
See the review paper Vivone et al.[1] for more details.
- Parameters:
y (deepinv.utils.TensorList) – input tensorlist of (MS, PAN)
- Returns:
Tensor of image pan-sharpening using the Brovey method.
- References: